Cu2Ge: a new 2D topological Semimetal
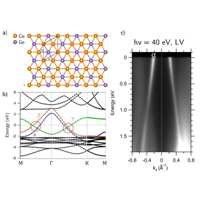 Among various metal/semiconductor systems, copper/germanium alloys have been studied since the 1990s to understand the formation mechanisms of Schottky barriers, fundamental to diodes of the same name. This system, which felt into disuse, has recently attracted renewed interest due to Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations. Indeed, these calculations predict that the 2D alloy Cu2Ge has a band structure with a 1D intersection of valence and conduction bands, characteristic of a topological semimetal with a Dirac nodal line. Members of the Spectroscopy of New Quantum States team at INSP have experimentally demonstrated for the first time that it is possible to synthesize Cu2Ge on a copper crystal and that its electronic structure exhibits the expected characteristics for the purely 2D case. Its properties make this alloy a promising candidate for high-frequency electronic applications and an ideal system for studying exotic properties that can emerge in nodal line materials.
Among various metal/semiconductor systems, copper/germanium alloys have been studied since the 1990s to understand the formation mechanisms of Schottky barriers, fundamental to diodes of the same name. This system, which felt into disuse, has recently attracted renewed interest due to Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations. Indeed, these calculations predict that the 2D alloy Cu2Ge has a band structure with a 1D intersection of valence and conduction bands, characteristic of a topological semimetal with a Dirac nodal line. Members of the Spectroscopy of New Quantum States team at INSP have experimentally demonstrated for the first time that it is possible to synthesize Cu2Ge on a copper crystal and that its electronic structure exhibits the expected characteristics for the purely 2D case. Its properties make this alloy a promising candidate for high-frequency electronic applications and an ideal system for studying exotic properties that can emerge in nodal line materials.
Légende :
a) Structure atomique de Cu2Ge. b) Structure de bande calculée par DFT. c) Spectre ARPES mesuré dans la direction r-K . Seule la bande α est visible dans ces conditions d’énergie de photons et de polarisation.
Reference
Synthesis and characterisation of Cu2Ge, a new two-dimensional Dirac nodal line semimetal
Cameau, Mathis; Olszowska, Natalia; Rosmus, Marcin; Silly, Mathieu G.; Cren, Tristan; Malecot, Axel; David, Pascal; D’angelo, Marie
2D Materials, 11 035023 (2024)
Contact
Marie D’angelo : dangelo(at)insp.jussieu.fr